■ 基本信息
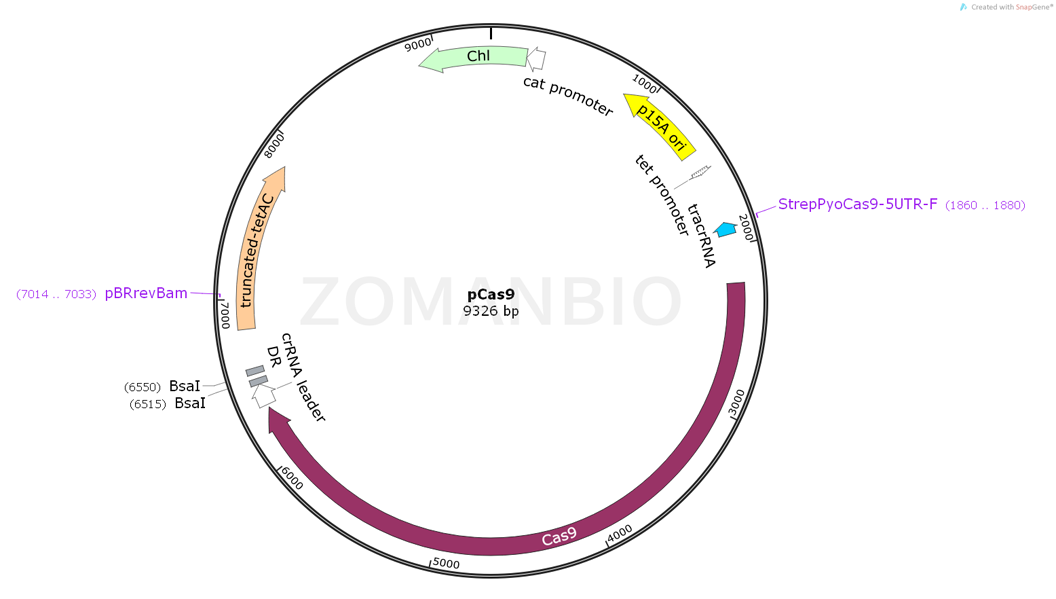
别名: | Plasmid #42876 |
复制子: | p15A ori |
质粒分类: | 大肠系列质粒;大肠编辑质粒;大肠Cas9质粒 |
质粒大小: | 9326bp |
原核抗性: | Chl |
克隆菌株: | Stbl3 |
培养条件: | 37℃ |
表达宿主: | 大肠杆菌 |
诱导方式: | 无需诱导 |
5'测序引物: | StrepPyoCas9-5UTR-F(CGGTGCCACTTTTTCAAGTTG) |
3'测序引物: | pBRrevBam(GGTGATGTCGGCGATATAGG) |
■ 质粒属性
质粒宿主: | 大肠杆菌 |
质粒用途: | 基因编辑 |
片段类型: |
|
片段物种: |
|
原核抗性: | 氯霉素 |
真核抗性: |
|
荧光标记: |
|
■ 质粒简介
pCas9质粒是CRISPR/Cas9系统类载体,复制子是p15A ori和ori,质粒大小是9326bp,可转化进相应的宿主细胞中,通大量养条件是LB,37℃。
pCas9 can often be difficult to target double-stranded breaks (DSBs) with the precision that is necessary for various genome editing applications. The ability to engineer Cas9 derivatives with purposefully altered PAM specificities would address this limitation. Here we show that the commonly used Streptococcus pyogenes Cas9 (SpCas9) can be modified to recognize alternative PAM sequences using structural information, bacterial selection-baseddirected evolution, and combinatorial design. CRISPR-Cas9 nucleases enable efficient genome editing in a wide variety of organisms and cell types . Target site recognition by Cas9 is programmed by a chimeric single guide RNA (sgRNA) that encodes a sequence complementary to a target protospacer5 , but also requires recognition of a short neighboring PAM . SpCas9, the most robust and widely used Cas9 to date, primarily recognizes NGG PAMs and is consequently restricted to sites that contain this motif . It can therefore be challenging to implement genome editing applications that require precision, such as: homology-directed repair (HDR), which is most efficient when DSBs are placed within 10–20 bps of a desired alteration; the introduction of variable-length insertion or deletion (indel) mutations into small size genetic elements such as microRNAs, splice sites, short open reading frames, or transcription factor binding sites by non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ); and allele-specific editing, where PAM recognition might be exploited to differentiate alleles.
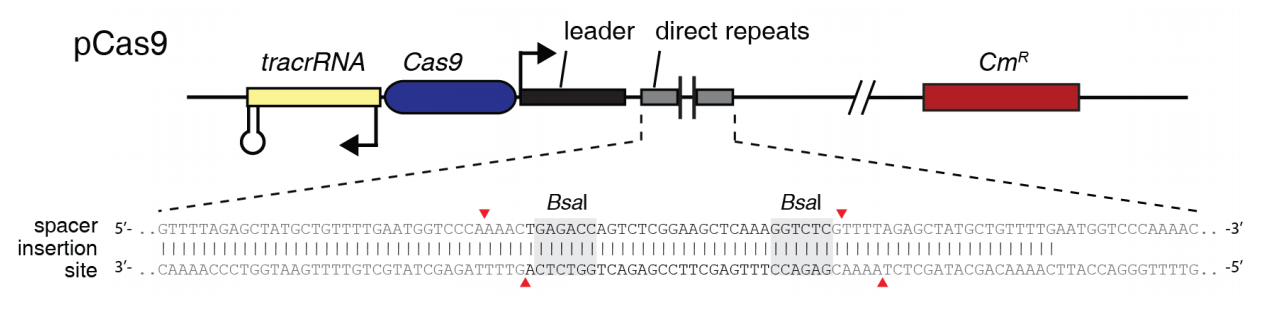
■ 质粒图谱
■ 质粒序列
质粒序列请下载: ZK1672 pCas9大肠敲除质粒.txt
ZK1672 pCas9大肠敲除质粒.txt